Four new subway lines will be built to link Beijing and neighboring Hebei province by 2021, as part of the region’s integrated development, Hebei’s top economic planner said.
 |
|
[China Daily]
|
The subway lines, together with other means of transportation, will cut the transfer time between the capital and cities in Hebei to less than 1 hour, according to a transportation plan released by the Hebei Development and Reform Commission for the 13th Five-Year Plan period (2016-20) period.
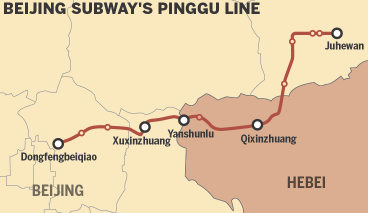
According to the plan, one of the four subways-the Pinggu Line-will link Beijing’s Pinggu and Tongzhou districts with Sanhe in Langfang, Hebei.
Preparatory work for the Pinggu Line has already started and is expected to be completed by 2021, according to the National Development and Reform Commission.
The other three lines, which are in the planning phase, would link Yizhuang in Beijing with downtown Langfang; Daxing in Beijing with Gu’an in Langfang; and Fangshan in Beijing with Zhuozhou in Baoding.
Development of the urban rail transportation system in the Beijng-Tianjin-Hebei region must be accelerated as there is significant demand for transportation services for short- and medium-distance journeys in the region, according to the plan.
By 2015, five cities in Hebei-Langfang, Cangzhou, Shijiazhuang, Baoding and Tangshan-had become part of a “one-hour traffic circle” connecting them to the capital.
However, large volumes of commuters traveling to and from Beijing every day require bus, subway or intercity railway services that provide faster and more frequent modes of transport.
To better meet demand, a 58-billion-yuan ($8.4 billion) investment will see the total length of the urban rail transportation system in Hebei, including lines connecting Beijing, reach 80 kilometers by 2020.
Intercity railway lines that connect Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei, not including subway lines, will be extended to a total of more than 400 km.
Intercity railway stations will be established mainly around Beijing’s new airport in Daxing district and Chongli in Zhangjiakou, a co-host of the 2022 Winter Olympics.
Construction of the stations is expected to guarantee convenient routes for passengers traveling between the new airport and Winter Olympics venues.
The upgrade of the transportation system will aid in moving Beijing’s noncapital functions, and the transfer of industries and people to Hebei, the plan said, adding that it will also create job opportunities and help develop the local economy.
“The system will make life more convenient for residents of the capital’s neighboring cities, which will attract more investment,” said Wang Yuling, an official at the Hebei Development and Reform Commission.
Fight with Cudgels (c.1820-1823), Francisco de Goya. Wikimedia Commons.




